The Concept of Bank Merger: Steps, Examples, and Implications
What is a bank merger?
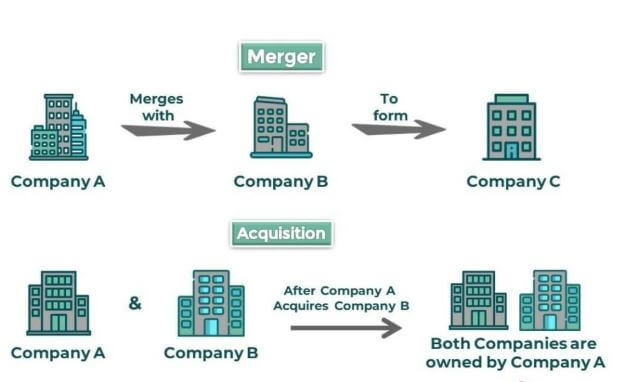
A bank merger is a corporate transaction in which two or more banks combine to form a single banking entity. The combination may take the form of one bank acquiring another (an acquisition), two banks joining as equals (a merger of equals), or multiple banks consolidating into a new entity (amalgamation). Mergers change ownership, control, balance-sheet structure, product offerings and—often—branch footprints.
Types of bank mergers
(Practical overlap exists; labels sometimes vary by jurisdiction.)
- Horizontal merger
- Two banks operating in the same line of business and often in overlapping geographical markets join (e.g., two retail banks in the same region).
- Vertical merger
- A bank combines with an entity at a different stage of the financial value chain (rare for regulated banks, more common where banks merge with non-banking financial services like brokerage or insurance under a financial group).
- Conglomerate merger
- Combination of banks that operate in unrelated markets or offer different product sets (less common among pure banking entities).
- Merger of equals
- Two banks combine and agree to shared governance; often marketed as a partnership of equals.
- Acquisition (absorption)
- One bank (the acquirer) buys another (the target); the target may be fully absorbed.
- Statutory amalgamation / scheme of arrangement
- A legal/statutory consolidation under specific laws where liabilities, assets and shareholders are combined into a new or existing entity.
- Asset purchase / purchase of business
- One bank buys specific assets and liabilities rather than the whole legal entity (used sometimes for troubled banks).
- Cross-border merger
- Banks from different countries combine—bringing extra regulatory, cultural and operational complexity.
Advantages of merger
For customers
- Wider product range: Combined banks can offer more services (investment, corporate, retail, digital).
- Larger branch & ATM network: Greater convenience and geographic coverage.
- Stronger balance sheet: May increase confidence in deposit safety and lending capacity.
- Better digital and service investment: Cost savings may free funds for tech and service improvements.
- Access to specialized services: e.g., corporate, wealth, trade finance that smaller bank lacked.
For bankers (management, shareholders, employees)
- Economies of scale: Lower unit cost of services (shared back office, IT).
- Increased market share & pricing power: Better competitive position.
- Diversified risk profile: Geographic and product diversification reduces concentration risk.
- Higher capital base: More resources to support lending and large deals.
- Cross-selling opportunities: Sell more products to the combined client base.
Disadvantages of merger
For customers
- Reduced competition: Could lead to worse pricing, higher fees, or lower interest rates on deposits.
- Service disruption: Systems migration and branch closures can create temporary problems.
- Loss of personal service: Local/relationship banking may decline as operations centralize.
- Data privacy concerns: Data sharing and integration may raise privacy or security risks.
For bankers (management, shareholders, employees)
- Job losses / redundancies: Cost-cutting typically reduces overlapping roles.
- Cultural clashes: Different corporate cultures often create friction and productivity loss.
- Integration risk & costs: IT, legal, and operational integration can be expensive and risky.
- Regulatory hurdles: Approvals take time and may impose constraints or divestitures.
- Shareholder dilution / valuation risk: If merger is funded by share exchange, share value may be volatile.
Step-by-step bank merger process
(High-level — local law and regulator specifics vary.)
- Strategic decision & preliminary evaluation
- Boards/senior management identify strategic rationale and perform initial screening (market fit, synergies).
- Preliminary meetings & non-binding offer
- Confidential discussions; non-disclosure agreements; initial (non-binding) offer or memorandum of understanding.
- Confidentiality and planning
- Create deal teams (commercial, legal, finance, IT, HR, compliance). Establish timeline & integration planning.
- Due diligence
- Thorough legal, financial, tax, operational, IT, credit, regulatory, AML/KYC, HR, and compliance due diligence—identify risks, liabilities, contingent exposures.
- Valuation & deal structuring
- Decide structure: share swap, cash purchase, asset purchase, amalgamation. Valuation methods: DCF, comparable transactions, book-value adjustments, multiples.
- Negotiation & definitive agreement
- Negotiate price, terms, representations & warranties, indemnities. Sign definitive merger/acquisition agreement.
- Regulatory & statutory approvals
- File with central bank/financial regulator, competition authority (antitrust), and possibly foreign regulators for cross-border deals. Obtain approvals for change of control and capital requirements.
- Shareholder approval
- If required, convene shareholder meetings and vote; comply with disclosure rules.
- Pre-closing preparations
- Prepare integration playbooks: IT migration, product rationalization, HR decisions (redundancy plans), brand strategy, communication plans for customers and employees.
- Closing
- Legal completion: shares transferred, funds exchanged, statutory filings made. Regulatory conditions satisfied.
- Post-merger integration (PMI)
- Execute integration plan: systems, policies, branches, product rationalization, cultural integration, compliance harmonization. Monitor KPIs and synergy realization.
- Post-implementation review
- Review outcomes against objectives, regulatory reporting, remediate issues.
Five real-world examples of bank mergers (well-known)
- J.P. Morgan & Chase Manhattan (2000) — formation of today’s JPMorgan Chase through merger of J.P. Morgan & Co. and Chase Manhattan (followed by later acquisitions).
- Bank of America & Merrill Lynch (2008) — large acquisition during the global financial crisis expanding investment banking and wealth management.
- Citicorp & Travelers Group (1998) — merger that formed Citigroup (a financial conglomerate combining banking and insurance/brokerage businesses).
- Wells Fargo & Wachovia (2008–2009) — Wells Fargo acquired Wachovia during the financial crisis, expanding its national footprint.
- Banco Santander & Abbey National (2004) — Santander’s UK expansion by acquiring Abbey National.
100 MCQs (multiple choice questions) with answers and brief explanations
Below are 100 MCQs covering definitions, types, processes, regulations, valuation, integration and examples. Each question has four choices (A–D), the correct answer, and a short explanation.
- What is a bank merger?
A. The opening of a new branch
B. The combination of two or more banks into one entity
C. A bank’s decision to change its logo
D. The sale of a loan portfolio only
Answer: B. Explanation: A merger combines banks into a single legal/economic entity. - Which merger type involves two banks operating in the same market?
A. Vertical
B. Horizontal
C. Conglomerate
D. Asset purchase
Answer: B. Explanation: Horizontal mergers occur between competitors in the same market. - Which of the following is a common motivation for bank mergers?
A. Increasing operating costs
B. Achieving economies of scale
C. Reducing market share
D. Increasing regulatory burden
Answer: B. Explanation: Banks merge to reduce per-unit costs and gain scale. - A ‘merger of equals’ implies:
A. One party buys all assets with cash.
B. Both firms combine with shared governance and roughly equal bargaining power.
C. The smaller bank absorbs the larger.
D. Shareholders are not involved.
Answer: B. Explanation: Merger of equals means roughly equal partners combining leadership. - Which regulatory approval is almost always required in a bank merger?
A. Local zoning approval
B. Central bank / financial regulator approval
C. Food safety authority approval
D. Sports commission approval
Answer: B. Explanation: Bank mergers need regulator approval to ensure safety, soundness and competition. - Which valuation method projects future cash flows and discounts them to present?
A. Comparable company analysis
B. Discounted Cash Flow (DCF)
C. Book value only
D. Rule of thumb multiple
Answer: B. Explanation: DCF estimates intrinsic value via discounted future cash flows. - What is a primary risk during post-merger integration (PMI)?
A. Increased branch openings
B. Integration failure (IT, culture)
C. Reduced compliance requirements
D. Guaranteed cost savings
Answer: B. Explanation: Integration failure is a major risk undermining merger benefits. - Which is an example of an asset purchase?
A. Buying all shares in a target company
B. Buying specific loans and deposits but not the legal entity
C. Signing a joint venture agreement
D. Issuing new shares to existing shareholders
Answer: B. Explanation: Asset purchase transfers selected assets/liabilities, not whole entity. - Which is a disadvantage of bank mergers for customers?
A. More product choices
B. Reduced competition and possible higher fees
C. More branches in their area
D. Stronger capital base
Answer: B. Explanation: Less competition can hurt customer pricing. - Which of the following is part of due diligence?
A. Party planning for staff
B. Legal, financial, IT and compliance assessment
C. Immediate firing of management
D. Ignoring outstanding litigation
Answer: B. Explanation: Due diligence assesses all material risks. - Cross-border mergers particularly require additional scrutiny because of:
A. Same time zones
B. Multiple regulators and legal systems
C. Fewer languages required
D. Lower costs always
Answer: B. Explanation: Different jurisdictions create regulatory/operational complexity. - Which method is commonly used to value a bank’s loan portfolio?
A. Discounted Cash Flow of future loan repayments only
B. Estimation using risk-adjusted yield and credit metrics
C. Counting number of loans only
D. Ignoring credit quality
Answer: B. Explanation: Portfolios are valued with risk and yield adjustments. - Which authority may require a competition review?
A. Central bank only
B. Competition / antitrust authority
C. Local chamber of commerce
D. Private rating agencies
Answer: B. Explanation: Antitrust bodies review mergers for anti-competitive effects. - A common cost-saving approach post-merger is:
A. Hiring more duplicate staff
B. Eliminating overlapping back-office functions
C. Building duplicate data centers
D. Doubling advertising budgets immediately
Answer: B. Explanation: Merged banks often consolidate back-office roles to cut costs. - Which document generally outlines the detailed legal terms of a merger?
A. Non-disclosure agreement (NDA)
B. Definitive merger or acquisition agreement
C. Job application form
D. Customer complaint letter
Answer: B. Explanation: Definitive agreement contains terms, conditions, warranties. - Which is NOT normally a driver of bank consolidation?
A. Seeking new markets
B. Regulatory pressure for capitalization
C. Desire to reduce diversification
D. Technology-driven efficiency needs
Answer: C. Explanation: Mergers usually increase diversification, not reduce it. - Which accounting item is often tested most closely in due diligence?
A. Company logo design costs
B. Loan loss provisions and asset quality
C. Employee coffee preferences
D. Office decor expenditure
Answer: B. Explanation: Loan loss provisions reflect credit risk and are critical in banking M&A. - If a merger is financed by issuing acquirer shares to target shareholders, this is called:
A. Cash consideration
B. Share-swap / stock consideration
C. Debt financing only
D. Asset liquidation
Answer: B. Explanation: Share-swap uses acquirer stock as payment. - Which of these is a post-merger human-resources issue?
A. Food safety compliance
B. Handling redundancies and retention of key staff
C. Changing regulator statutes
D. Building a new logo
Answer: B. Explanation: HR must manage redundancies and retain talent. - What is goodwill in a merger context?
A. Tangible asset only
B. The excess of purchase price over fair value of net identifiable assets
C. Regulatory capital requirement
D. Branch network expansion
Answer: B. Explanation: Goodwill captures intangibles like brand, customer relationships. - Which of the following is an immediate customer-facing risk in a merger?
A. Instant increase in interest rates across the country
B. Disruption from IT systems migration
C. A new tax law
D. None—customers are never affected
Answer: B. Explanation: IT migrations can disrupt online banking, payments. - An asset purchase used to resolve a failing bank often involves:
A. Buying a sports team
B. Purchase of deposits and selected assets by a healthy bank
C. Immediate merger of both boards
D. No regulatory involvement
Answer: B. Explanation: Regulators sometimes arrange asset purchases to protect depositors. - Which is a typical synergy targeted in bank mergers?
A. Increased rent per branch
B. Revenue cross-sell and cost reduction from consolidation
C. Higher standalone operating cost
D. Increased back-office duplication
Answer: B. Explanation: Revenue synergies and cost synergies justify many deals. - Which metric often used to assess merger impact on earnings is:
A. EPS accretion/dilution
B. Number of branches closed
C. Date of incorporation
D. CEO’s travel expenses
Answer: A. Explanation: Earnings-per-share (EPS) accretion or dilution is used to assess financial impact. - Which regulator role is central in approving bank mergers?
A. Sports regulator
B. Financial sector supervisor / central bank
C. Ministry of tourism
D. Environmental regulator only
Answer: B. Explanation: Central bank/financial supervisor assesses safety and soundness. - What does ‘pre-merger due diligence’ primarily aim to do?
A. Entertain the board
B. Identify material liabilities and opportunities
C. Immediately fire all employees
D. Ignore legal exposures
Answer: B. Explanation: Due diligence identifies financial, legal, operational risks and values. - Which of the following is a regulatory concern in mergers?
A. Cultural fit only
B. Systemic risk and concentration of financial institutions
C. Dialogue with customers only
D. Logo color choice
Answer: B. Explanation: Regulators worry about concentration and systemic risk. - ‘Amalgamation’ in many jurisdictions means:
A. Temporary partnership for one month
B. Legal consolidation of two or more entities into a new entity
C. A single branch merger
D. Closing a bank permanently without replacement
Answer: B. Explanation: Amalgamation creates a new legal entity combining parties. - Which of the following is NOT typically part of integration planning?
A. IT migration roadmap
B. Brand and communication strategy
C. Employee retention and severance plans
D. Immediate deletion of customer accounts without notice
Answer: D. Explanation: Deleting customer accounts would be illegal/irresponsible. - Which financial ratio is most relevant when assessing a bank’s capital adequacy pre-merger?
A. Price/Earnings ratio
B. Common Equity Tier 1 (CET1) ratio
C. Inventory turnover
D. Gross margin of clothes sales
Answer: B. Explanation: CET1 measures bank capital strength. - What is an EPS-accretive merger?
A. A merger that reduces earnings per share
B. A merger that increases earnings per share for the acquirer
C. A merger where earnings stay constant
D. A type of HR policy
Answer: B. Explanation: EPS-accretive increases acquirer’s EPS post-deal. - ‘Material adverse change’ clause typically appears where?
A. Employee handbook
B. In the merger agreement to protect buyer if target’s condition worsens between signing and closing
C. Only in tax forms
D. In the customer terms and conditions only
Answer: B. Explanation: MAC clauses allow renegotiation or walkaway for big negative changes. - Which document is commonly used to start public disclosure of a bank merger?
A. Press release and regulatory filings
B. Internal email only
C. Customer text messages only
D. Social media memes
Answer: A. Explanation: Material transactions require public and regulatory disclosure. - In mergers, ‘delta’ of cost synergies refers to:
A. The combined revenue before costs
B. Expected cost savings from integration
C. Number of new products only
D. Branch profit margin only
Answer: B. Explanation: Cost synergy delta quantifies expected cost reductions. - Which of the following is a potential downside for bankers (employees) after merger?
A. More team-building events
B. Job redundancy and layoffs
C. Increased social media followers
D. Higher holiday allowance guaranteed
Answer: B. Explanation: Overlapping roles often lead to redundancies. - Which of these is an example of non-financial due diligence?
A. Cash flow forecasting
B. Culture and HR practices review
C. Valuation using DCF
D. Stock split analysis
Answer: B. Explanation: Cultural fit and HR practices are non-financial but crucial. - What is a divestiture in merger context?
A. Buying additional assets post-merger
B. Selling or spinning-off parts of the business to satisfy regulators or strategy
C. Terminating the merger agreement for no reason
D. Immediate closure of all branches
Answer: B. Explanation: Divestitures reduce concentration or misfit assets. - A ‘share-for-share exchange ratio’ determines:
A. The number of employees retained
B. How many acquirer shares each target share converts to
C. Branch opening dates
D. The regulator’s fees
Answer: B. Explanation: Exchange ratio sets share conversion terms. - Which integration issue affects customer experience most?
A. Office paint choices
B. ATM and online banking system compatibility and downtime
C. Corporate party location
D. Executive bonuses only
Answer: B. Explanation: Banking systems directly affect customer transactions. - What is ‘regulatory capital’ primarily used to measure?
A. Marketing effectiveness
B. Bank’s ability to absorb losses and operate safely
C. Employee satisfaction
D. Branch footfall
Answer: B. Explanation: Regulatory capital cushions losses to protect depositors. - Which valuation approach is often used for banks besides DCF?
A. Comparable transactions / price-to-book multiples
B. Retail inventory method
C. Real estate capitalization only
D. Social media followers valuation
Answer: A. Explanation: Banks are often valued on price-to-book or comparable deals. - What does AML stand for in bank M&A due diligence?
A. Asset Management Loan
B. Anti-Money Laundering
C. Annual Marketing Liability
D. Asset Migration Lead
Answer: B. Explanation: AML checks are crucial to avoid legal/regulatory risks. - Which of the following is true about cross-border mergers?
A. Require fewer approvals than domestic deals
B. Often require approvals from multiple national regulators
C. Are always simpler than domestic mergers
D. Never involve cultural integration challenges
Answer: B. Explanation: Multiple regulators and laws complicate cross-border deals. - When a merger increases market concentration, regulators may:
A. Ignore the merger
B. Require remedies such as divestitures or reject the deal
C. Increase employees’ salaries
D. Mandate a new logo
Answer: B. Explanation: Antitrust regulators can impose conditions or block deals. - Which item is likely a confidentiality tool during negotiations?
A. Job offer letter
B. Non-disclosure agreement (NDA)
C. Public press release
D. Marketing brochure
Answer: B. Explanation: NDA protects sensitive information during talks. - What is the role of external advisers in bank M&A?
A. Provide coffee during meetings
B. Provide legal, tax, accounting, financial and regulatory advice
C. Buy a stake automatically
D. Replace management without consent
Answer: B. Explanation: Advisers guide valuation, structure and regulatory process. - Which of the following is an example of integration cost?
A. Cost of printing annual reports only
B. IT migration and severance payments
C. Interest paid on customer loans
D. ATM withdrawal charges
Answer: B. Explanation: Integration has direct costs like IT work and severance. - A merged bank’s brand strategy could be:
A. Maintain both brands indefinitely without harmonization
B. Rebrand under a single new or dominant brand after review
C. Never communicate changes to customers
D. Close all branches immediately without notice
Answer: B. Explanation: Brands are usually unified strategically; communication is key. - Which measure helps ensure data integrity in systems migration?
A. Ignoring backups
B. Robust testing, reconciliation and parallel run periods
C. Migrating without testing to save time
D. Deleting old records immediately
Answer: B. Explanation: Testing and parallel runs reduce migration risk. - Which of these is a regulatory condition sometimes imposed post-merger?
A. Increase in CEO’s pay
B. Maintain certain branch presence or capital levels
C. Close all branches in specified regions immediately
D. Eliminate all compliance functions
Answer: B. Explanation: Regulators may require commitments on capital, lending or branch presence. - Which item is most likely to create negative goodwill?
A. Buying a bank at a price lower than fair value of identifiable net assets
B. Overpaying for a bank resulting in high goodwill
C. Buying office furniture
D. Issuing new shares
Answer: A. Explanation: Negative goodwill arises when purchase price < fair value net assets. - Which metric assesses loan portfolio quality?
A. Non-performing loan (NPL) ratio
B. Social media engagement rate
C. Branch opening speed
D. Number of ATM transactions only
Answer: A. Explanation: NPL ratio measures credit quality and risk. - What is an “earnout” in M&A?
A. Mandatory closure of branches
B. Contingent payment to sellers based on future performance
C. A type of loan product
D. A legal fine imposed by the regulator
Answer: B. Explanation: Earnouts tie part of payment to future targets. - Which of the following is a potential positive effect of mergers on shareholders?
A. Reduced diversification always
B. Potential increase in shareholder value from synergies
C. Guaranteed increased dividends forever
D. Immediate job guarantees for all staff
Answer: B. Explanation: Successful mergers can produce shareholder value via synergies. - Which of these is a common integration KPI?
A. Number of new brands launched unrelated to banking
B. Cost-synergy realization and customer retention rates
C. CEO’s lunch bill
D. Number of press statements issued only
Answer: B. Explanation: KPIs measure synergy capture and customer impact. - Which term describes the buyer’s protection against undisclosed liabilities?
A. Indemnity and representations & warranties in the purchase agreement
B. A marketing slogan
C. An employee manual
D. Public relations plan
Answer: A. Explanation: Warranties and indemnities allocate risk and offer protection. - Which is an advantage of a stock-for-stock transaction?
A. Immediate cash outflow for the acquirer
B. Preserves acquirer cash and aligns seller’s interest with combined entity
C. Results in immediate regulatory rejection always
D. Guarantees no share dilution
Answer: B. Explanation: Stock consideration spares cash and aligns incentives. - Which is typically required to approve a takeover of a publicly listed bank?
A. Merely a handshake
B. Shareholder vote per company law and stock exchange rules
C. A new product launch
D. Closing all competitor branches
Answer: B. Explanation: Shareholder approval and compliance with listing rules are required. - In a distressed-bank asset purchase, who usually arranges the deal?
A. A sports federation
B. Deposit insurer or regulator
C. Local chamber of commerce
D. A private charity only
Answer: B. Explanation: Regulators or deposit insurers manage resolution of failing banks. - Which of the following can be a cultural integration strategy?
A. Imposing one culture without engagement
B. Active engagement, leadership alignment and joint events to set culture
C. Ignoring employee sentiment entirely
D. Immediate mass layoffs only
Answer: B. Explanation: Active culture work helps reduce friction and retain talent. - Which financial statement item often needs restatement during due diligence?
A. Office temperature readings
B. Loan loss provisions and off-balance-sheet items
C. Company’s social media policy
D. Number of coffee machines
Answer: B. Explanation: Provisions and contingent items materially affect value. - Which of these is a common regulatory filing required?
A. Merger application to central bank/financial regulator
B. Local business license for a cafe
C. Passport application for executives only
D. Library membership
Answer: A. Explanation: Formal merger applications are a regulatory requirement. - Which is true about goodwill amortization under IFRS?
A. Goodwill is amortized every year
B. Goodwill is not amortized but tested annually for impairment
C. Goodwill is immediately expensed in all cases
D. Goodwill is recorded as inventory
Answer: B. Explanation: Under IFRS, goodwill is impairment-tested, not amortized. - Which of these is a likely reason for regulators to refuse a merger?
A. Too much marketing investment planned
B. Concerns over market dominance creating anti-competitive environment
C. Too many branches being kept open
D. A long name chosen for the new bank
Answer: B. Explanation: Antitrust concerns can lead to rejection. - What is a “break fee” in merger agreements?
A. Fee for coffee breaks during meetings
B. Compensation payable if one party walks away from a signed deal under certain conditions
C. Payment to regulators for faster approvals
D. A fee paid by customers for early loan repayment
Answer: B. Explanation: Break fees discourage breaking agreements and compensate the other party. - Which of the following is a market risk relevant in bank mergers?
A. Change in regulatory policy that affects future profitability
B. Employee commute distance
C. Number of logos available
D. Office furniture quality
Answer: A. Explanation: Policy changes can materially affect expected returns. - Which of these is an advantage of acquiring a smaller regional bank?
A. Immediate closing of all markets
B. Fast access to regional client base and deposit franchise
C. Loss of any local knowledge
D. Increased regulatory penalties by default
Answer: B. Explanation: Acquisitions can provide local market entry and deposits. - Which of these typically increases as a result of a successful merger?
A. Overhead per unit
B. Scale economies reducing cost per transaction
C. Number of redundant systems per function
D. Number of standalone HR policies forever
Answer: B. Explanation: Successful mergers lower unit costs via scale. - Which of the following is a typical timeline hurdle in bank mergers?
A. Instant integration in 1 day always
B. Regulatory review periods and shareholder approvals extending timelines
C. Mergers are always complete within 24 hours
D. No need for planning
Answer: B. Explanation: Regulatory and shareholder steps lengthen timeline. - Which of the following is a post-merger Customer communication best practice?
A. No communication until changes are final
B. Clear, frequent communication about what changes customers will experience and when
C. Communicate only to selected VIPs
D. Replace all customer service staff without notice
Answer: B. Explanation: Transparent communication minimizes customer churn and confusion. - Which of the following can be a regulatory condition for cross-border merger approval?
A. Appointing a local representative or maintaining local capital
B. Reducing capital to zero
C. Immediate exit from the market
D. Closing all branches in home country
Answer: A. Explanation: Regulators may require local commitments for supervision. - Which of these is an example of revenue synergy?
A. Reducing staff meals
B. Cross-selling new financial products to the combined customer base
C. Firing top sales staff immediately
D. Closing profitable lines of business
Answer: B. Explanation: Revenue synergies come from selling more to existing customers. - Which due diligence area focuses on compliance with laws and past legal disputes?
A. IT due diligence
B. Legal due diligence
C. HR due diligence only
D. Marketing due diligence only
Answer: B. Explanation: Legal due diligence investigates contracts, litigation, regulatory history. - What is the principal purpose of a merger integration steering committee?
A. To organize parties’ after-merger celebration only
B. To oversee and coordinate integration activities across functions
C. To replace auditors permanently
D. To design new logos only
Answer: B. Explanation: Steering committees govern PMI and resolve cross-functional issues. - Which entity often supervises cross-border banking group resolution planning?
A. Local sports authority
B. Home and host country regulators and resolution authorities
C. Tourism boards
D. Retail customers only
Answer: B. Explanation: Multiple regulators coordinate for cross-border resolution. - Which of these is most likely to require change management in a merger?
A. Integrating payroll, processes, IT and culture
B. Nothing—change happens automatically
C. Only branding changes matter
D. Only external communications change, nothing internal
Answer: A. Explanation: Change management is needed across many internal domains. - Which of the following best describes ‘price-to-book ratio’ use in bank valuation?
A. It’s irrelevant for banks
B. Commonly used to compare market value against net asset value for banks
C. Only used for manufacturing firms
D. Indicates number of books sold
Answer: B. Explanation: Price-to-book is a standard banking valuation metric. - Which is a likely effect on interest rates offered post-merger in less competitive markets?
A. Deposit rates rise universally
B. Deposit rates may fall and loan rates may rise due to lower competition
C. No possible change at all
D. All customers get same rate regardless of market dynamics
Answer: B. Explanation: Reduced competition can worsen pricing for customers. - What is the role of a fairness opinion in M&A?
A. A marketing slogan
B. Independent adviser’s view that transaction terms are fair to shareholders
C. A regulatory license
D. A document for customers only
Answer: B. Explanation: Fairness opinions help boards demonstrate reasonableness of price/terms. - Which of these is true about integration of IT systems?
A. It’s the fastest, easiest part of integration
B. It is complex, costly, and high-risk; requires planning & testing
C. It can be ignored entirely
D. Only mobile apps need integration
Answer: B. Explanation: IT integrations are often the most complex and risky. - Which of these items should be examined to assess credit risk pre-merger?
A. Historical NPLs, provisioning policies and concentration exposures
B. Office desk sizes
C. Number of cafeterias only
D. Staff holiday schedules only
Answer: A. Explanation: Credit metrics reveal potential problem loans and concentration risks. - Which of the following is a post-merger cost that might reduce early benefits?
A. Implementation of integrated IT security and remedial fixes
B. Immediate revenue doubling without costs
C. No costs at all—only gains
D. Free insurance coverage for all customers forever
Answer: A. Explanation: Integration costs can temporarily reduce net gains. - Which of the following best describes a legal ‘scheme of arrangement’?
A. A marketing tactic
B. A court-approved process to reorganize or combine companies under statute
C. A casual handshake deal
D. A type of branch lease agreement
Answer: B. Explanation: Schemes are statutory, often used for complex consolidations. - Which step usually follows signing of the definitive agreement?
A. Closing immediately without any conditions
B. Satisfying closing conditions, obtaining regulatory and shareholder approvals before closing
C. Starting a new unrelated business immediately
D. Ignoring all regulatory requirements
Answer: B. Explanation: Deals typically close after conditions precedent are fulfilled. - Which of the following is an example of contingent liability discovered during due diligence?
A. Pending litigation that might cause material fines
B. Office plant watering schedule
C. Logo color code
D. Staff book club membership
Answer: A. Explanation: Pending litigation poses contingent obligations. - Which of these is a likely due diligence outcome that could change the deal price?
A. Discovery of off-balance-sheet liabilities or underestimated loan losses
B. Finding more coffee machines than expected
C. Discovering a nicer meeting room
D. Slightly different office paint shade
Answer: A. Explanation: Material liabilities lead to price adjustments or termination. - Which of the following is a reason shareholders of a target bank may reject a merger?
A. The offer undervalues the target or unfavourable terms
B. They dislike the acquirer’s logo color only
C. They want more holidays for employees only
D. The merger reduces regulatory oversight
Answer: A. Explanation: Shareholders vote against unfair offers. - Which of these is an advantage of a bank acquiring technology capability through merger?
A. Slower product development
B. Faster digital transformation and access to new platforms
C. Automatic regulatory approval without review
D. Guaranteed elimination of competitor banks
Answer: B. Explanation: Acquiring tech-savvy banks accelerates digital offerings. - Which of these is a typical remedy if antitrust concerns arise?
A. Forced rebranding only
B. Divestiture of branches or business lines to preserve competition
C. Firing the board of directors automatically
D. Reducing the number of ATMs to zero
Answer: B. Explanation: Divestitures restore competitive balance sometimes required by regulators. - Which of these is a sign of successful merger integration?
A. Synergies captured on time and budget; customer attrition minimal
B. Doubling of redundant systems left in place
C. Major customer outages without remedy
D. No monitoring of KPIs post-close
Answer: A. Explanation: Timely synergy capture and low customer loss indicate success. - What is an important privacy consideration in systems integration?
A. Data mapping and regulatory compliance for data transfers across jurisdictions
B. Only the color of user interface matters
C. No need to consider regulations
D. Deleting customer records immediately improves privacy
Answer: A. Explanation: Data protection laws affect how customer data migrates and is stored. - Which of the following is central to the regulator’s safety assessment?
A. The new bank’s marketing plan only
B. Capital adequacy and risk management systems
C. The number of branches in remote areas only
D. Only the combined logos
Answer: B. Explanation: Regulators focus on capital and robust risk management. - Which of the following is a common contractual protection sellers seek?
A. Full immunity from all future claims always
B. Limitations on post-closing indemnities and survival periods for representations
C. No payment at closing
D. Obligation to close the target’s branch the next day
Answer: B. Explanation: Sellers negotiate caps and durations for liabilities post-closing. - Which of these is often part of financial modelling for a merger?
A. Forecasting cost synergies, revenue synergies and standalone performance
B. Choosing the office furniture color scheme
C. Predicting regulator’s mood only
D. Ignoring tax consequences
Answer: A. Explanation: Models estimate synergies and combined entity performance. - Which of the following is likely part of the integration communications plan?
A. No communications at all to avoid leaks
B. Timely messages to customers, staff and regulators about expected changes and timelines
C. Only internal communications with no customer updates
D. Only regulatory filings, no customer-facing messages
Answer: B. Explanation: Transparent communications reduce confusion and attrition. - Which of these is an example of legal structure used in mergers?
A. Amalgamation creating a new entity, acquisition by share purchase, asset purchase, or scheme of arrangement
B. Instant change of country without permission
C. Creating a new sport league
D. Only verbal agreements without paperwork
Answer: A. Explanation: Multiple legal structures exist for transactions. - Which of the following helps retain customers during a merger?
A. Clear communication, preserving account terms and reliable service during migration
B. Radical immediate closure of accounts without notice
C. Reducing all customer service hours permanently
D. Removing online access entirely
Answer: A. Explanation: Communication and service continuity reduce churn. - Which of these is true about bank merger accounting treatment?
A. Purchase accounting is typically used: acquirer recognizes assets and liabilities at fair value, records goodwill if purchase price exceeds net assets
B. No accounting entries are required
C. Goodwill is always immediately expensed to the income statement under all standards
D. Assets remain at target’s historical cost without change
Answer: A. Explanation: Purchase method / acquisition accounting is standard. - Which of these is a typical barrier to achieving projected synergies?
A. Complete agreement between all employees immediately
B. Integration delays, retention failures, regulatory conditions and unforeseen costs
C. Instant approval from all banks worldwide
D. Zero integration planning needed
Answer: B. Explanation: Realizing synergies often faces practical obstacles. - Which of the following best summarizes the ultimate success factor in bank mergers?
A. Size of the new logo
B. Effective planning and execution of integration, regulatory approval and preservation of customer trust
C. Number of legal disclaimers only
D. Closing branches only to reduce costs regardless of customers
Answer: B. Explanation: Strategic rationale plus strong execution determines long-term success.