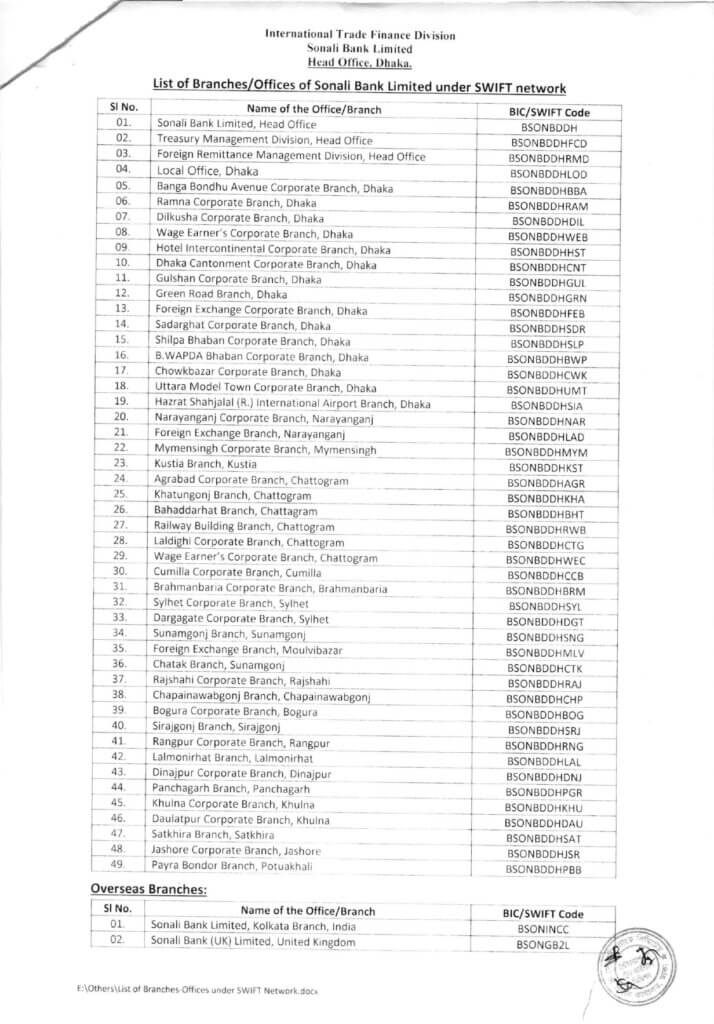
Swift code of Sonali Bank PLC
Sonali Bank PLC has various branches, and many of the larger or specialized branches may have their own unique, 11-character SWIFT codes (e.g., BSONBDDHWEB, BSONBDDHCNT, BSONBDDHFEB).
-
BSONBDDH (or BSONBDDHXXX) is the Head Office code and is generally the safe choice if you are unsure of the specific branch code.
-
For international transfers, it is always best to confirm the exact SWIFT code with the specific branch or the recipient to ensure the funds are routed correctly and without delay.
| BSONBDDHAGR | CHITTAGONG | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHBBA | DHAKA | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHBHT | CHITTAGONG | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHBOG | BOGRA | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHBRM | BRAHMANBARIA | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHBWP | DHAKA | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHCCB | COMILLA | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHCHP | CHAPAINAWABGANJ | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHCNT | DHAKA | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHCTG | CHITTAGONG | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHCTK | SUNAMGANJ | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHCWK | DHAKA | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHDAU | KHULNA | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHDGT | SYLHET | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHDHN | DHAKA | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHDIL | DHAKA | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHDNJ | DINAJPUR | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHFCD | DHAKA | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHFEB | DHAKA | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHGRN | DHAKA | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHGUL | DHAKA | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHHST | DHAKA | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHJSR | JESSORE | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHKHA | CHITTAGONG | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHKHU | KHULNA | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHKST | KUSHTIA | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHLAD | NARAYANGANJ | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHLAL | RANGPUR | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHLOD | DHAKA | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHMLV | MOULVIBAZAR | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHMYM | MYMENSINGH | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHNAR | NARAYANGANJ | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHRAJ | RAJSHAHI | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHRAM | DHAKA | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHRNG | RANGPUR | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHRWB | CHITTAGONG | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHSAT | SATKHIRA | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHSDR | DHAKA | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHSLP | DHAKA | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHSNG | SUNAMGANJ | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHSRJ | SIRAJGANJ | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHSYL | SYLHET | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHWEB | DHAKA | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHWEC | CHITTAGONG | SONALI BANK PLC |
| BSONBDDHXXX | DHAKA | SONALI BANK PLC |
SWIFT Code BSONBDDHBOG Breakdown
- SWIFT Code
- BSONBDDHBOG
Sonali Bank PLC SWIFT CODE - Bank Code
- BSON – code assigned to SONALI BANK PLC
- Country Code
- BD – code belongs to Bangladesh
- Location Code
- DH – code represents the institution location
- Code Status
- H – H means active code
- Branch Code
- BOG – code indicates this is a branch office
- Head Office
- BSONBDDH – primary office of SONALI BANK PLC, Bangladesh.
-
The SWIFT code is immensely important because it is the foundation for virtually all secure, standardized international money transfers between banks worldwide.1
Here is a breakdown of its key importance:
1. 🌐 Unique Global Identification
The SWIFT code (also known as a BIC or Bank Identifier Code) is a unique international ID for a specific bank and, often, a specific branch.2
-
SWIFT stands for Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication.3
-
The code identifies the Bank, the Country, the City, and the specific Branch (if 11 characters are used).4
-
Example: For Sonali Bank PLC, BSONBDDH breaks down the bank (BSON), the country (BD), and the location (DH).
2. 🔒 Security and Standardization
SWIFT is a global messaging network, not a money transfer system itself.5 Its importance lies in the standardized, secure way it allows banks to communicate.6
-
Secure Messaging: The network ensures payment instructions are sent between the sender’s bank and the recipient’s bank in a secure, encrypted, and globally accepted format.7
-
Accuracy: The standardized code structure eliminates ambiguity, ensuring the correct bank and branch receive the payment instruction.8
3. 🚀 Routing and Efficiency
Without the SWIFT code, international transfers would be slow, manual, and prone to error.9
-
Routing: It acts like an international zip code for financial institutions, telling the sending bank exactly where to route the payment message.10
-
Error Reduction: The precision built into the code minimizes the risk of payments being delayed, rejected, or sent to the wrong institution.11
4. ⚖️ Role in International Commerce
Any person or business involved in international trade, remittances, or cross-border payments relies on SWIFT codes.12
-
Receiving Payments: If you are receiving money from a foreign country, the sender must have your bank’s SWIFT code.13
-
Sending Payments: If you are sending money overseas, you must have the recipient’s bank’s SWIFT code.14
Key Distinction: SWIFT Code vs. Account Number
It’s important to remember what the SWIFT code doesn’t do:
Code Type Purpose Identifies SWIFT Code (BIC) International Bank Transfer Routing The Bank/Branch Account Number (or IBAN) The Final Destination of the Funds The Specific Account held by the customer You generally need both the SWIFT code and the account number to successfully complete an international wire transfer.15
The SWIFT code is essential for standardizing and securing international bank communication, the resulting SWIFT transfer system has several notable disadvantages compared to modern alternatives, especially for smaller or time-sensitive payments.1
Here are the main disadvantages of using the SWIFT code system for money transfers:
1. 💰 High and Non-Transparent Costs
The most common disadvantage is the high cost, which can often be hidden and complex.2
-
Multiple Fees: A SWIFT transfer typically involves fees from the sending bank, the receiving bank, and any intermediary banks (also called correspondent banks) the payment passes through.3 Each bank in the chain can deduct a fee.4
-
Hidden Exchange Rate Markups: Banks often use less competitive exchange rates than the mid-market rate, applying a “markup” that reduces the final amount the recipient receives.5 This can be the largest hidden cost.6
-
Unpredictable Final Amount: Because intermediary fees are often unknown to the sender, the recipient may receive a smaller amount than expected, which is a major transparency issue.
2. 🐢 Slow Processing Time
SWIFT transfers are not instant and can take several days to complete.7
Processing Delays: Transfers typically take 1 to 5 business days.8 This is much slower than domestic transfers or modern instant payment systems.9
-
Intermediary Banks: If the sending and receiving banks don’t have a direct relationship, the payment must be routed through one or more intermediary banks, which adds processing time and fees at each stop.10
-
Compliance and Checks: Every bank in the chain performs regulatory checks (Know Your Customer/Anti-Money Laundering), which can delay the funds further, especially for payments to certain countries or for unusual amounts.11
-
Weekends and Holidays: Transfers stop moving on weekends and public holidays in any of the countries involved in the routing chain.12
3. 📉 Lack of Real-Time Tracking
Historically, a major frustration was the lack of visibility once the payment was sent.13
-
Limited Visibility: Traditional SWIFT transfers offered poor tracking, making it difficult to know exactly where the money was, or which bank was causing a delay.
-
Note: SWIFT has addressed this with SWIFT GPI (Global Payments Innovation), which provides much better tracking and often faster speeds. However, not all banks or transfers use the GPI standard yet.
4. 📝 High Risk of Error/Rejection
Even a small error in the instructions can lead to major delays and additional fees.14
-
Manual Data Entry: Errors in the SWIFT code, account number, or recipient name can cause the transfer to be stopped, investigated, or rejected by an intermediary bank, often resulting in additional penalty fees charged to the sender or recipient for correction.
-
Complexity: The requirement to use an exact 8-character or 11-character code for the correct branch adds a layer of complexity not present in simpler payment systems.
In summary, the SWIFT system, while global and reliable, is often expensive, slow, and non-transparent for the end user, which is why newer FinTech and regional payment systems (like SEPA in Europe) have emerged to address these specific issues.
Would you like to know more about the SWIFT GPI system that tries to solve some of these issues?
Do you have another question about international banking or a specific SWIFT code you’d like to check?
-

