Commercial Invoice
Feature of Commercial Invoice :
In international trade, a commercial invoice is an essential document that facilitates the smooth flow of goods and ensures compliance with customs regulations. A commercial invoice serves as a record of the transaction between the buyer and the seller, providing important details about the goods being shipped. In this article, we will explore the features of a commercial invoice and its significance in international trade.

Introduction
International trade involves the exchange of goods and services between different countries. To ensure a transparent and organized trade process, various documents are required, and one such document is a commercial invoice. A commercial invoice is a crucial component of international trade transactions as it provides critical information for customs authorities, shipping agents, and financial institutions.
Definition of a Commercial Invoice
A commercial invoice is a legal document issued by the seller to the buyer that outlines the details of the goods or services being sold. It includes information such as the quantity, description, value, and terms of the goods, along with payment details and shipping instructions. This document serves as evidence of the transaction and helps determine the appropriate duties, taxes, and fees to be levied on the imported goods.
Importance of a Commercial Invoice
The commercial invoice holds significant importance for various stakeholders involved in international trade. Here are some key reasons why a commercial invoice is essential:
- Clear Communication: A commercial invoice ensures clear and accurate communication between the buyer, seller, and other parties involved in the trade process. It provides a detailed breakdown of the goods, their quantities, and associated costs.
- Customs Compliance: Customs authorities require a commercial invoice to assess the value of imported goods and determine applicable duties and taxes. A well-prepared commercial invoice helps streamline the customs clearance process and minimizes the risk of delays or penalties.
- Payment Verification: For international transactions, a commercial invoice serves as proof of the agreed-upon terms and conditions, including payment details. It enables the buyer to verify the accuracy of the invoice before making payment, ensuring transparency and trust between the parties.
- Record Keeping: Commercial invoices serve as essential records for both buyers and sellers. They provide a documented history of the transaction, including product details, pricing, and payment terms. These records are valuable for financial reporting, audits, and dispute resolution.
Key Components of a Commercial Invoice
A commercial invoice typically includes the following key components:
- Invoice Header: The top section of the invoice containing the seller’s and buyer’s contact information, invoice number, and date of issuance.
- Shipping Details: Information about the shipment, including the origin and destination addresses, mode of transport, and expected delivery date.
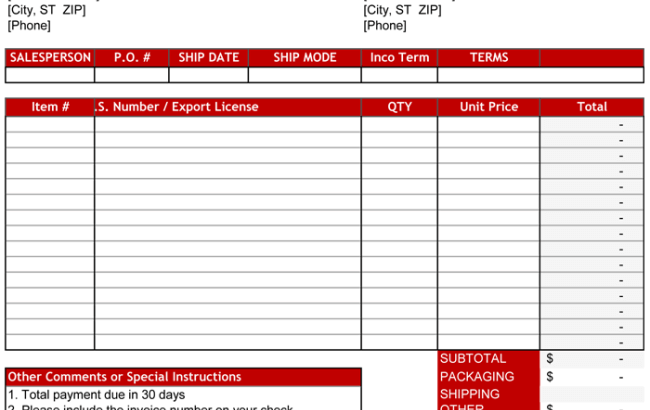
- Itemized Description: A detailed description of each item being sold, including quantity, unit price, total value, and any applicable discounts or taxes.
- Terms of Sale: The agreed-upon terms and conditions, including payment terms, delivery terms, and any additional terms specific to the transaction.
- Payment Information: Details about the accepted payment methods, due dates, and any other relevant payment instructions.
- Signatures: The signatures of authorized representatives from both the buyer and the seller, indicating agreement and acceptance of the terms.
Purpose of a Commercial Invoice
The primary purpose of a commercial invoice is to provide a comprehensive overview of the goods or services being sold in an international trade transaction. It serves the following purposes:
- Customs Declaration: A commercial invoice helps customs authorities accurately assess the value of imported goods, determine applicable duties and taxes, and ensure compliance with import regulations.
- Payment Verification: It serves as proof of the agreed-upon terms and conditions, ensuring that the buyer and seller are on the same page regarding the products, quantities, and pricing.
- Legal Compliance: Commercial invoices fulfill legal requirements imposed by governments and international trade organizations. They help prevent fraud, protect intellectual property rights, and promote fair trade practices.
- Dispute Resolution: In the event of a dispute or disagreement, a commercial invoice provides a documented record of the transaction, making it easier to resolve conflicts and address any issues that may arise.
Legal Requirements for a Commercial Invoice
Different countries have specific legal requirements for commercial invoices. It is crucial to understand and comply with these requirements to avoid customs delays and penalties. Here are some common legal requirements:
- Accurate and Complete Information: Commercial invoices must contain accurate and complete information about the goods being shipped, including their description, quantity, value, and any applicable codes or classifications.
- Language and Currency: Invoices should be prepared in the language of the importing country or in a language agreed upon by the buyer and seller. The currency used should be clear and consistent.
- Invoice Copies: It may be necessary to provide multiple copies of the commercial invoice, depending on the country’s requirements. These copies are often used by customs authorities, shipping agents, and financial institutions.
- Additional Documentation: Some countries may require additional supporting documents, such as certificates of origin, packing lists, or licenses. It is important to research and comply with the specific requirements of the importing country.
How to Create a Commercial Invoice
Creating a commercial invoice is an important step in international trade. It ensures that all necessary information is accurately documented for customs clearance, payment verification, and legal compliance. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to create a commercial invoice:
- Header Information: Start by including your company’s name, address, and contact details at the top of the invoice. This information should be clearly visible and easily identifiable.
- Invoice Number and Date: Assign a unique invoice number to the document and include the date of issuance. This helps in organizing and tracking invoices for record-keeping purposes.
- Buyer and Seller Information: Provide the contact information of both the buyer and the seller, including names, addresses, phone numbers, and email addresses. This ensures that the invoice is correctly addressed to the relevant parties.
- Description of Goods or Services: Provide a detailed description of the goods or services being sold. Include information such as product names, quantities, unit prices, and any relevant codes or classifications. Be specific and use clear language to avoid any ambiguity.
- Total Amount Due: Calculate the total amount due for the goods or services, including any applicable taxes, discounts, or additional charges. Clearly state the currency in which the payment should be made.
- Payment Terms: Specify the agreed-upon payment terms, including the due date and accepted payment methods. This helps ensure a smooth transaction and avoids any confusion or delays in payment.
- Shipping and Delivery Details: If applicable, include information about shipping and delivery, such as the shipping method, estimated delivery date, and any tracking numbers or references. This provides transparency and helps the buyer and seller track the shipment.
- Additional Charges or Terms: If there are any additional charges, such as customs duties or handling fees, or any specific terms or conditions related to the transaction, include them in a separate section. This ensures that all aspects of the agreement are clearly stated.
- Notes or Comments: Add any additional notes or comments that may be relevant to the transaction. This could include special instructions, warranties, or any other important information that the buyer or seller should be aware of.
- Terms and Conditions: Include a section that outlines the terms and conditions of the sale. This may cover topics such as liability, dispute resolution, and any applicable legal or trade regulations. Ensure that these terms and conditions are clear and concise.
- Signature and Date: Provide space for authorized representatives from both the buyer and the seller to sign and date the commercial invoice. This indicates agreement and acceptance of the terms and conditions stated in the invoice.
- Attachments and Supporting Documents: If required, attach any supporting documents to the commercial invoice, such as certificates of origin, packing lists, or licenses. Ensure that these documents are accurately referenced in the invoice.
- Review and Proofread: Before finalizing the commercial invoice, thoroughly review the document for accuracy and completeness. Check for any errors or inconsistencies and make necessary revisions.
- Save and Distribute: Save a copy of the completed commercial invoice for your records. Distribute the invoice to the buyer and any other relevant parties involved in the transaction, such as customs authorities or financial institutions.
By following these steps, you can create a well-prepared commercial invoice that accurately represents the details of the international trade transaction. Remember to comply with any specific legal requirements of the importing and exporting countries to ensure a smooth customs clearance process.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Commercial Invoices
While preparing commercial invoices, it is important to avoid common mistakes that can lead to complications or delays in international trade. Here are some mistakes to watch out for:
- Inaccurate or Incomplete Information: Ensure that all the information on the invoice is accurate, complete, and matches the supporting documentation. Mistakes or missing details can result in customs delays or rejection of the shipment.
- Incorrect Valuation: Properly assess the value of the goods being sold and accurately state it on the invoice. Incorrect valuation can lead to disputes with customs authorities and potential penalties.
- Lack of Consistency: Maintain consistency in product descriptions, quantities, and pricing across all relevant documents, including the invoice, packing list, and certificates of origin. Inconsistencies can raise suspicion and cause delays in customs clearance.
- Missing or Improper Signatures: Obtain the necessary signatures from authorized representatives of both the buyer and the seller. Missing signatures can raise questions about the authenticity and validity of the invoice.
- Neglecting Legal Requirements: Familiarize yourself with the legal requirements of the importing and exporting countries. Failure to comply with these requirements can result in fines, delays, or even the rejection of the goods.
Benefits of Using Commercial Invoice Software
Using commercial invoice software can significantly streamline the invoicing process and offer several benefits, including:
- Efficiency: Commercial invoice software automates calculations, reduces manual data entry, and generates professional-looking invoices quickly. This saves time and ensures accuracy.
- Compliance: Many commercial invoice software solutions come with built-in compliance checks, helping you adhere to legal requirements and avoid costly mistakes.
- Customization: Invoice templates in commercial invoice software can be customized to match your branding, allowing you to maintain a professional image.
- Record Keeping: Commercial invoice software often includes features for organizing and storing invoices digitally. This simplifies record keeping and makes it easier to retrieve and track invoices when needed.
- Integration: Some commercial invoice software integrates with other business systems such as accounting software, making the invoicing process seamless and reducing manual data entry.
Tips for Effective Commercial Invoice Management
To ensure smooth commercial invoice management, consider the following tips:
- Organize and Label: Maintain a systematic approach to invoice management by organizing invoices in a logical manner. Use clear labels or categories to easily identify and retrieve invoices when necessary.
- Implement a Tracking System: Use a tracking system or software to monitor the status of invoices, including payment due dates and pending approvals. This helps in tracking the progress of invoices and ensures timely payment.
- Establish Clear Communication Channels: Maintain open lines of communication with the buyer, seller, and any other relevant parties involved in the trade. Promptly address any invoice-related queries or concerns to avoid delays or misunderstandings.
- Monitor Payment Status: Regularly track the payment status of invoices to ensure timely payments. Follow up with the buyer if there are any delays or discrepancies.
- Periodic Review: Conduct periodic reviews of your invoicing process to identify areas for improvement. Analyze any recurring issues and implement measures to enhance efficiency and accuracy.
Role of Commercial Invoices in International Trade
Commercial invoices play a crucial role in facilitating international trade. Some key roles include:
- Customs Clearance: Customs authorities rely on commercial invoices to verify the contents and value of imported goods. Accurate commercial invoices expedite the customs clearance process and ensure compliance with customs regulations.
- Trade Financing: Commercial invoices serve as supporting documentation for trade financing. Banks and financial institutions often require commercial invoices to assess the risk and extend credit to importers or exporters.
- Taxation and Duties: Commercial invoices help determine the appropriate taxes, duties, and fees levied on imported goods. Governments use the information provided in commercial invoices to enforce tax regulations and ensure fair trade practices.
- Trade Data and Statistics: Commercial invoices contribute to the compilation of trade data and statistics. This information helps governments, trade organizations, and businesses analyze trade patterns, identify market trends, and make informed decisions.
- Dispute Resolution: In the event of disputes or discrepancies, commercial invoices serve as evidence to resolve conflicts between the buyer and the seller. They provide a documented record of the agreed-upon terms and conditions.
How Commercial Invoices Impact Customs Clearance
Commercial invoices have a significant impact on the customs clearance process. Here’s how they influence customs procedures:
- Determining Duties and Taxes: Customs authorities use commercial invoices to assess the value of imported goods and calculate the applicable duties and taxes. Accurate and detailed commercial invoices help avoid delays or disputes during the customs clearance process.
- Risk Assessment: Customs officials analyze commercial invoices to identify any potential risks associated with the imported goods. Incomplete or inconsistent information can raise suspicions and result in additional inspections or delays.
- Compliance with Import Regulations: Commercial invoices must comply with the import regulations of the destination country. Failure to provide the necessary information or meet specific requirements can lead to customs clearance issues or even the rejection of the goods.
- Supporting Documentation: Commercial invoices serve as supporting documentation for other customs-related documents, such as certificates of origin or import licenses. They provide essential information to validate the authenticity and legality of the trade transaction.
Ensuring Accuracy and Compliance in Commercial Invoices
To ensure accuracy and compliance in commercial invoices, follow these best practices:
- Double-Check Information: Review the commercial invoice for accuracy and completeness before issuing it. Verify that all details, such as product descriptions, quantities, and pricing, are consistent with the supporting documentation.
- Stay Updated on Legal Requirements: Stay informed about the legal requirements of both the exporting and importing countries. Research and understand the specific regulations governing commercial invoices to avoid non-compliance.
- Maintain Clear Communication: Maintain clear and open lines of communication with the buyer and any other relevant parties. Confirm any ambiguous details or specifications to avoid misunderstandings that could affect the accuracy of the invoice.
- Standardize Invoice Templates: Use standardized invoice templates that include all the necessary fields and comply with legal requirements. This ensures consistency and makes it easier to review and process invoices.
- Seek Professional Assistance: If you’re unsure about the legal requirements or face complex trade transactions, seek professional assistance from customs brokers or trade experts. Their expertise can help ensure accuracy and compliance with commercial invoices.
Conclusion
Commercial invoices are essential documents in international trade. They provide a detailed account of the goods or services being sold and serve various purposes, including customs declaration, payment verification, and legal compliance. Creating accurate and compliant commercial invoices is crucial for smooth customs clearance and trade facilitation. By following best practices, using commercial invoice software, and staying updated on legal requirements, businesses can streamline their invoicing process, minimize errors, and ensure compliance with international trade regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the difference between a commercial invoice and a proforma invoice? A commercial invoice is issued after the sale has taken place and includes the final agreed-upon details and pricing. On the other hand, a proforma invoice is issued before the sale as a preliminary invoice that outlines the goods or services, their estimated cost, and other relevant information.
2. Can a commercial invoice be used for domestic transactions? While commercial invoices are commonly associated with international trade, they can also be used for domestic transactions. Commercial invoices provide a comprehensive record of the transaction details, making them useful for both domestic and international sales.
3. Are electronic commercial invoices accepted by customs authorities? Many customs authorities accept electronic commercial invoices, provided they meet certain criteria. It’s important to check the specific requirements of the importing country to ensure compliance with their regulations regarding electronic documentation.
4. Is a commercial invoice a legally binding document? Although a commercial invoice is an important document in the trade process, it is not inherently a legally binding agreement. However, it serves as evidence of the agreed-upon terms and conditions between the buyer and the seller, which can be used to resolve disputes or claims.
5. How long should commercial invoices be retained for record-keeping purposes? It is advisable to retain commercial invoices for a minimum of five years for record-keeping purposes. However, it is important to consult local regulations or legal requirements, as some countries may have specific guidelines regarding record retention for trade-related documents.
The invoice is the list of articles containing their particulars and prices. It is also book-keeping instruments for the importer.
i. The description of the good / Merchandise in invoice should corresponds with to that given in the L/C.Sample Commercial Invoice:
1. EXPORTER
2. CONSIGNEE
3. INTERMEDIATE CONSIGNEE
4. FORWARDING AGENT
5. COMMERCIAL INVOICE NO
6. CUSTOMER PURCHASE ORDER NO.
7. B/L, AWB NO.
8. COUNTRY OF ORIGIN
9. DATE OF EXPORT
10. TERMS OF PAYMENT
11. EXPORT REFERENCES
12. AIR/OCEAN PORT OF EMBARKATION
13. EXPORTING CARRIER/ROUTE
14. PACKAGES
15. QUANTITY
16. NET WEIGHT/GROSS WEIGHT
17. DESCRIPTION OF MERCHANDISE
18. UNIT PRICE/TOTAL VALUE
19. PACKAGE MARKS
20. MISC. CHARGES
21. CERTIFICATIONS
ii. The invoice should be signed by the beneficiary or by the assignee and it should be prepared strictly as per credit terms and condition of L/C be incorporated in the LC.
iii.The amount of invoice should be expressed in the currency of the L/C.
iv. The invoice should specify quantity clearly and the word like approximately, about, nearly be avoided.
v. The invoice should contain brief reference to transport documents and disclose basis of pricing (FOB, CFR, CIF etc.).vi. The invoice documents do not include extraordinary expenses such as cable, storage, commission, etc. unless specified in the credit. vii. The relevant LCAF number, Bangladesh Bank registration number, etc. are correctly incorporated in the invoice.
Type of Invoice :
01.Commercial Invoice
There is no standard form of an invoice. Each exporter designs commercial invoice form in his own way. A commercial invoice is required to be duly signed by the exporter.02.Consular Invoice
It is made out on a prescribed format certified by the consular office of the importing country stationed in the exporting country. It is also called a legalized invoice. A consular invoice is a type of commercial document that is sometimes required for international trade transactions, especially for certain countries. It is prepared by the exporter and certified by the consulate or embassy of the importing country. The purpose of a consular invoice is to provide additional verification and authentication of the transaction details, ensuring compliance with the customs regulations and import requirements of the destination country. Here are some key points to know about consular invoices:- Definition and Purpose: A consular invoice is a document that provides a detailed description of the goods being exported, including their value, quantity, and other relevant information. It is primarily used to verify the accuracy of the commercial invoice and to ensure compliance with the import regulations and duties of the destination country.
- Consulate or Embassy Certification: Unlike a regular commercial invoice, a consular invoice requires certification by the consulate or embassy of the importing country. This certification confirms that the details provided in the invoice are accurate and complete.
- Country-Specific Requirements: The need for a consular invoice and the specific requirements vary from country to country. Some countries have made consular invoices mandatory for certain goods or above a certain value threshold, while others may not require them at all. It is important to research and understand the specific requirements of the importing country before preparing a consular invoice.
- Information Included: A consular invoice typically includes information similar to that of a commercial invoice, such as the names and addresses of the buyer and seller, a description of the goods, their value, quantity, and other relevant details. It may also require additional information specific to the importing country’s regulations.
- Certification Process: The certification process for a consular invoice usually involves submitting the document, along with any required supporting documents, to the consulate or embassy of the importing country. The consulate or embassy will review the invoice for accuracy and compliance with their regulations before providing the necessary certification.
- Fees and Processing Time: Consular invoices may be subject to fees for certification, and the processing time can vary depending on the workload of the consulate or embassy. It is advisable to inquire about the fees and processing time in advance to ensure timely submission and avoid any delays in the export process.
- Importance of Accuracy: Like any other trade document, accuracy is crucial when preparing a consular invoice. The information provided must be precise, consistent, and in line with the supporting documents. Any discrepancies or inaccuracies can lead to delays, penalties, or even the rejection of the shipment by customs authorities.
- Additional Documentation: In addition to the consular invoice, other supporting documents may be required by the importing country. These can include certificates of origin, packing lists, insurance certificates, and other relevant trade documents. It is important to ensure that all required documents are prepared and submitted along with the consular invoice.
It is worth noting that the use of consular invoices has become less common in recent years, as many countries have transitioned to electronic systems and rely more on other trade documents and customs procedures. However, for countries that still require consular invoices, it is important to understand and comply with the specific requirements to facilitate a smooth export process.
03. Custom Invoice
A customs invoice, also known as a customs declaration or commercial invoice, is a crucial document used in international trade. It provides detailed information about the goods being imported or exported, their value, and other relevant details required by customs authorities. The customs invoice serves several purposes, including assessing import duties and taxes, facilitating customs clearance, and ensuring compliance with trade regulations. Here’s what you need to know about creating a customs invoice:
- Basic Information: Start by including the basic information at the top of the invoice. This includes your company’s name, address, and contact details, as well as the recipient’s information.
- Invoice Number and Date: Assign a unique invoice number and include the date of issuance. This helps in organizing and tracking invoices for record-keeping purposes.
- Description of Goods: Provide a detailed description of the goods being imported or exported. Include information such as product names, quantities, unit prices, and any relevant codes or classifications. Be specific and use clear language to avoid any ambiguity.
- Value of Goods: State the value of the goods in the designated currency. This should reflect the actual transaction value or an acceptable valuation method as per customs regulations.
- Currency: Specify the currency in which the invoice amount is expressed. This helps customs authorities in accurately assessing import duties and taxes.
- Origin of Goods: Indicate the country of origin for the goods. The country of origin is important for determining preferential treatment under free trade agreements and assessing import duties.
- Terms of Sale: Include the terms of sale, such as Incoterms (e.g., EXW, FOB, CIF) or any specific agreements between the buyer and seller regarding the responsibility for transportation, insurance, and other costs.
- Payment Terms: Specify the agreed-upon payment terms, including the due date and accepted payment methods.
- Additional Charges: If there are any additional charges, such as shipping costs, insurance fees, or handling charges, clearly state them separately.
- Declaration: Include a declaration statement confirming the accuracy and authenticity of the information provided in the invoice. This declaration also asserts that the goods comply with applicable laws and regulations.
- Authorized Signature: The invoice should be signed by an authorized representative of the exporting or importing company, certifying the accuracy of the information provided.
- Attachments and Supporting Documents: Attach any supporting documents required by customs authorities, such as packing lists, certificates of origin, or licenses. Refer to these documents within the invoice to establish a clear link between the invoice and the supporting paperwork.
- Proofread and Review: Before finalizing the customs invoice, carefully proofread the document for accuracy and completeness. Ensure that all the required information is included and that there are no errors or discrepancies.
- Retain Copies: Keep copies of the customs invoice for your records. These copies are essential for reference, accounting, and potential audits.
Creating a well-prepared customs invoice is crucial for a smooth customs clearance process. Ensure compliance with customs regulations, accurately document the details of the goods being imported or exported, and provide the necessary information for customs authorities to assess duties and taxes appropriately. By following these guidelines, you can facilitate efficient customs procedures and maintain compliance with international trade regulations.
These are specific forms supplied by the customs office of the respective importer duly filled & signed by the shipper & serve the purpose of making easy entry of the merchandise into the importing country.04.Certified Invoice
It is an invoice bearing a signed statement by someone in the importers country who has inspected the goods & found them in accordance with those specified in the contract. A certified invoice is a document that has been verified and authenticated by a designated authority to ensure its accuracy and authenticity. This certification provides an added level of credibility and reliability to the invoice, making it a valuable tool in international trade transactions. Here’s what you need to know about certified invoices:- Certification Process: The certification process for a certified invoice involves submitting the document to a designated authority, such as a notary public or a chamber of commerce. The authority will review the invoice, verify the information provided, and authenticate the document by stamping or signing it.
- Purpose and Benefits: The purpose of a certified invoice is to provide assurance to the buyer and other parties involved in the transaction that the information stated in the invoice is accurate and valid. A certified invoice can help build trust, facilitate smoother transactions, and reduce the risk of disputes or misunderstandings.
- Information Included: A certified invoice contains detailed information about the goods or services being sold, including descriptions, quantities, prices, and any additional charges or terms. It may also include the names and addresses of the buyer and seller, the invoice number and date, and any applicable payment terms.
- Certification Authority: The authority responsible for certifying invoices may vary depending on the country or region. In some cases, a notary public or a government entity may perform the certification, while in others, it may be done by a chamber of commerce or a trade association.
- Legal Validity: A certified invoice holds legal validity and can be used as evidence in case of disputes or legal proceedings. The certification adds weight to the invoice’s authenticity and strengthens its position as a legally recognized document.
- International Trade Considerations: Certified invoices are particularly important in international trade, where parties may not have direct knowledge or trust in each other. The certification provides an independent verification of the invoice’s accuracy, which can be crucial when dealing with unfamiliar buyers or sellers.
- Fees and Processing Time: The certification of an invoice may involve fees charged by the certification authority. The fees can vary depending on the jurisdiction and the complexity of the certification process. It is advisable to inquire about the fees and processing time in advance.
- Supporting Documents: Along with the certified invoice, it may be necessary to provide supporting documents to the certification authority. These documents can include contracts, purchase orders, shipping documents, or any other relevant paperwork that validates the transaction.
- Confidentiality and Data Protection: It is essential to ensure the confidentiality and protection of sensitive information included in the invoice. The certification authority should have measures in place to safeguard.
- Cross-Border Recognition: Certified invoices often hold cross-border recognition, meaning they are accepted and respected by authorities in different countries. This recognition is particularly valuable when conducting international trade, as it helps facilitate customs procedures, validate the transaction, and comply with regulations in multiple jurisdictions.
- Dispute Resolution: In case of any disputes or disagreements between the buyer and seller, a certified invoice can serve as crucial evidence. The certification acts as an impartial validation of the invoice’s content, providing a solid foundation for resolving conflicts and reaching a fair resolution.
- Building Trust and Reputation: By opting for a certified invoice, businesses demonstrate their commitment to transparency and reliability. This commitment helps build trust with customers, suppliers, and other stakeholders, contributing to a positive reputation in the market. Trusted invoicing practices can lead to repeat business, referrals, and stronger business relationships.
- Compliance with Legal Requirements: Depending on the country or industry, certain legal requirements may mandate the use of certified invoices in specific situations. It is essential for businesses to stay informed about any such obligations and ensure compliance to avoid penalties or legal repercussions.
- Electronic Certification: With the advent of digital technologies, electronic certification of invoices has become more prevalent. Electronic certification offers convenience, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional paper-based processes. It often involves the use of digital signatures or electronic seals to authenticate the invoice’s content.
- Certification for Different Purposes: Certified invoices can serve various purposes beyond customs and legal compliance. They may be required for specific industries, such as healthcare or government contracts, where additional regulations or standards apply. In such cases, specialized certification bodies or authorities may be involved.
- Integration with Digital Platforms: Many businesses now rely on digital platforms and software for invoicing and financial management. Some platforms offer built-in features for certification or integration with certification services, streamlining the certification process and ensuring the invoices are digitally signed or sealed.
- Future Trends: As technology continues to advance, the certification of invoices is likely to evolve as well. Blockchain technology, for instance, holds the potential to revolutionize the certification process by providing an immutable and transparent record of invoice certifications, further enhancing trust and security.
- Seeking Professional Assistance: Certifying an invoice may involve complex procedures, legal considerations, and compliance requirements. It is advisable for businesses to seek professional assistance, such as consulting with legal experts, certified public accountants, or certification service providers, to ensure the process is conducted accurately and in line with applicable regulations.
- In conclusion, a certified invoice plays a significant role in international trade, providing assurance, credibility, and legal validity to the invoicing process. It demonstrates a commitment to transparency, helps build trust, and facilitates smooth transactions. By understanding the importance of certified invoices and complying with certification requirements, businesses can strengthen their invoicing practices, mitigate risks, and foster successful trade relationships.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q1: Can any invoice be certified? A: Not all invoices require certification. The need for certification depends on specific legal requirements, industry regulations, or cross-border considerations.
Q2: Who can provide certification for invoices? A: Certification can be provided by designated authorities such as notaries public, chambers of commerce, certification bodies, or government entities, depending on the jurisdiction and the purpose of certification.
Q3: What supporting documents may be required for invoice certification? A: Supporting documents may include contracts, purchase orders, shipping documents, certificates of origin, or any other relevant paperwork that validates the transaction and supports the information provided in the invoice.
Q4: How long is a certified invoice valid? A: The validity period of a certified invoice can vary depending on local regulations, industry practices, or specific contractual agreements. It is advisable to consult relevant authorities or legal experts to determine the applicable validity period.
Q5: Is electronic certification of invoices legally recognized? A: Electronic certification is increasingly being recognized and accepted in many jurisdictions. However, the legal recognition of electronic certification may vary depending on the country and applicable regulations. It is important to comply with local laws and consult with legal experts to ensure compliance.
05.Pro forma Invoice
Pro forma invoices play a crucial role in international trade, serving as preliminary documents that outline the details of a potential sale or transaction. While they are not legally binding like a commercial invoice, pro forma invoices provide valuable information to both the buyer and seller. Here’s a comprehensive guide on pro forma invoices:
- Definition and Purpose: A pro forma invoice is a preliminary document issued by the seller to the buyer, providing a detailed breakdown of the goods or services being offered. Its purpose is to facilitate negotiations, outline the terms of the potential transaction, and provide an estimate of costs.
- Provisional Nature: Pro forma invoices are non-binding and do not represent an actual sale. Instead, they serve as a quotation or proposal that outlines the terms and conditions under which the seller is willing to proceed with the transaction.
- Detailed Description: The pro forma invoice should include a detailed description of the goods or services, including quantities, specifications, unit prices, and any applicable discounts. This information helps the buyer understand the offering and make an informed decision.
- Payment Terms: Clearly state the payment terms, including the currency, payment methods, and any specific conditions or deadlines. This allows the buyer to assess the financial aspects of the potential transaction.
- Validity Period: Specify the validity period of the pro forma invoice to ensure that the terms and prices remain valid for a reasonable duration. This helps avoid any confusion or discrepancies if the buyer decides to proceed with the purchase at a later date.
- Shipping and Delivery Details: If applicable, provide information on shipping methods, estimated delivery times, and any associated costs. This assists the buyer in evaluating the logistics and planning for the receipt of the goods or services.
- Taxes and Duties: Clearly indicate whether taxes, customs duties, or other additional charges are included in the pro forma invoice or if they will be calculated separately. This ensures transparency and helps the buyer assess the total cost of the transaction.
- Terms and Conditions: Include any specific terms and conditions that govern the potential sale, such as warranties, return policies, or liability limitations. Clearly outlining these terms helps manage expectations and prevent misunderstandings.
- Company Information: Provide the seller’s complete company information, including name, address, contact details, and any applicable tax identification or registration numbers. This allows the buyer to verify the seller’s credibility and contact them if necessary.
- Logo and Branding: Incorporate the seller’s logo and branding elements into the pro forma invoice. This helps establish brand identity and professionalism, creating a positive impression on the buyer.
- Revision and Customization: Pro forma invoices can be revised or customized based on the buyer’s requirements or negotiation outcomes. This flexibility allows for adjustments to the terms, quantities, or prices before finalizing the actual sale.
- Clarity and Accuracy: Ensure that the pro forma invoice is clear, accurate, and free from any errors or inconsistencies. Double-check all calculations, product descriptions, and terms to provide an error-free document.
- Communication and Follow-up: Maintain effective communication with the buyer throughout the negotiation process. Address any questions or concerns promptly and provide any additional information or documentation as required.
- Transition to Commercial Invoice: If the buyer agrees to proceed with the transaction outlined in the pro forma invoice, a commercial invoice is typically issued to finalize the sale. The commercial invoice will include the actual sale details, quantities, prices, and other necessary information.
Pro forma invoices are valuable tools for initiating and facilitating international trade transactions. By providing essential details and outlining the terms and conditions of a potential sale, pro forma invoices help both buyers and sellers make informed decisions and establish a foundation for successful business relationships.
It is a form of quotation to a potential buyer.